Common frog
Scientific name
The common frog is known scientifically as Pelophylax perezi
Family
It belongs to the family Ranidae, which includes many species of frogs.
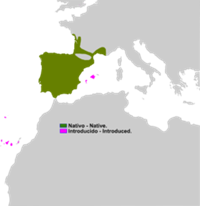
Distribution and Habitat
Common frogs are found in various parts of Europe, from northern Europe to mountainous regions in the south. They are also found in some areas of Asia. They inhabit a variety of aquatic habitats, such as ponds, lakes, streams and wetlands. They are usually found near water bodies during the breeding season and in wooded terrestrial areas during the rest of the year.
Behaviour
Common frogs are amphibians and have a dual life on land and in water. They are known for their distinctive song during the mating season, which is often a loud, repetitive sound. During winter, they may hibernate in shelters underground or at the bottom of bodies of water.
Feeding Habits
Common frogs are carnivorous and feed on a varied diet that includes insects, worms, spiders and other invertebrates. They are active predators and hunt prey with their sticky tongue.
Reproduction
Common frog reproduction involves the laying of eggs in bodies of water. Females lay eggs in gelatinous clusters that adhere to aquatic vegetation. After hatching, the aquatic larvae develop into tadpoles and undergo metamorphosis into adult frogs. During the mating season, males emit calls to attract females.
Common frogs play an important role in aquatic ecosystems and help control insect populations. They are known for their distinctive song and are a symbol of the arrival of spring in many regions.