Running Toad
Scientific name
The common toad is scientifically known as Epidalea calamita.
Family
It belongs to the family Bufonidae, which includes several species of toads.
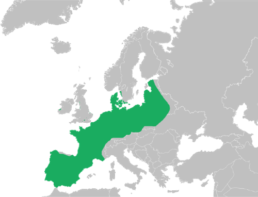
Distribution and Habitat
The common toad is found in various parts of Europe, from north-western Europe to regions of southern Europe. They inhabit a variety of habitats, such as wet meadows, wooded areas and coastal areas. They are often associated with areas with seasonal water, such as temporary ponds and small water bodies.
Behaviour
Runner toads are nocturnal amphibians and tend to be active at night. During the day, they tend to hide in cool, damp shelters, such as under logs or rocks. They are known for their rough skin and variable colouring, which can range from green to brown.
Feeding Habits
Runner toads are carnivorous and feed on a variety of prey, including insects, spiders, worms and other invertebrates. They capture prey with their sticky tongue.
Reproduction
The reproduction of the racer toad involves the laying of eggs in bodies of water, such as temporary ponds. Females lay eggs that form a gelatinous chain in the water. After hatching, the aquatic larvae develop into tadpoles and undergo metamorphosis to become adult toads. During the mating season, males emit calls to attract females.
These toads are an important part of aquatic ecosystems and help in the control of insect populations. Conservation of their aquatic habitats is essential for their survival.