Viperine snake
Scientific name
The viperine snake is scientifically known as Natrix maura.
Family
It belongs to the family Colubridae, which includes a wide variety of non-venomous snakes.
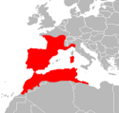
Distribution and Habitat
The viperine snake is found in various parts of Europe, including the Iberian Peninsula and some areas of France and northwest Africa. It inhabits aquatic habitats, such as streams, rivers, ponds and wetlands. It is a semi-aquatic snake that is comfortable both in water and on land.
Behaviour
The viperine snake is known for its defensive behaviour. When it feels threatened, it may flatten its neck and raise its head, similar to how venomous vipers do, hence its common name. However, it is a non-venomous snake and its bite is not dangerous to humans.
Feeding Habits
These snakes are carnivorous and feed primarily on aquatic prey such as fish, frogs and tadpoles. They may also consume small mammals and birds that come near water.
Reproduction
The viperine snake’s breeding season usually occurs in spring. They lay eggs in hidden nests near water. The young hatch from the eggs and are independent from birth.
It is important to note that despite its defensive behaviour and snake-like appearance, the viperine snake is harmless to humans and is an important component of the aquatic ecosystem in which it is found.