European fallow deer
Scientific name
The common fallow deer is scientifically known as Dama dama.
Family
It belongs to the family Cervidae, which includes other cervids such as deer and elk.
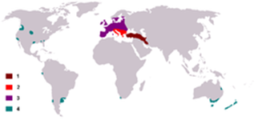
Location
Fallow deer are native to regions of Europe and western Asia, but have also been introduced to other parts of the world, including North America, South America, New Zealand and Australia. They are adapted to a variety of habitats, from woodland to grassland.
Behaviour
Fallow deer are social animals that tend to form groups called “clans” composed of females and their young. Adult males, called “stags”, are usually solitary, but join groups of females during the breeding season, known as the “rut”. They are known for their branched antlers that shed and regrow each year.
Feeding Habits
They are herbivores and feed mainly on grasses, leaves, shoots, twigs and fruits. Their diet may vary according to the availability of food in their habitat and the season.
Reproduction
The reproduction of fallow deer is usually linked to specific seasons. Females, called “hinds”, have a calving season in spring or summer, and give birth to one or two young, called “young fallow deer” or “bucks”. The males compete for the right to mate with the females during the rutting season, which is called the “rut”. During this period, males emit vocalisations and exhibit territorial behaviour to attract females.
Fallow deer are a species prized for their beauty and elegance, and are often found in game reserves and protected natural areas. Their management and conservation are important to maintain healthy populations in their natural habitat.