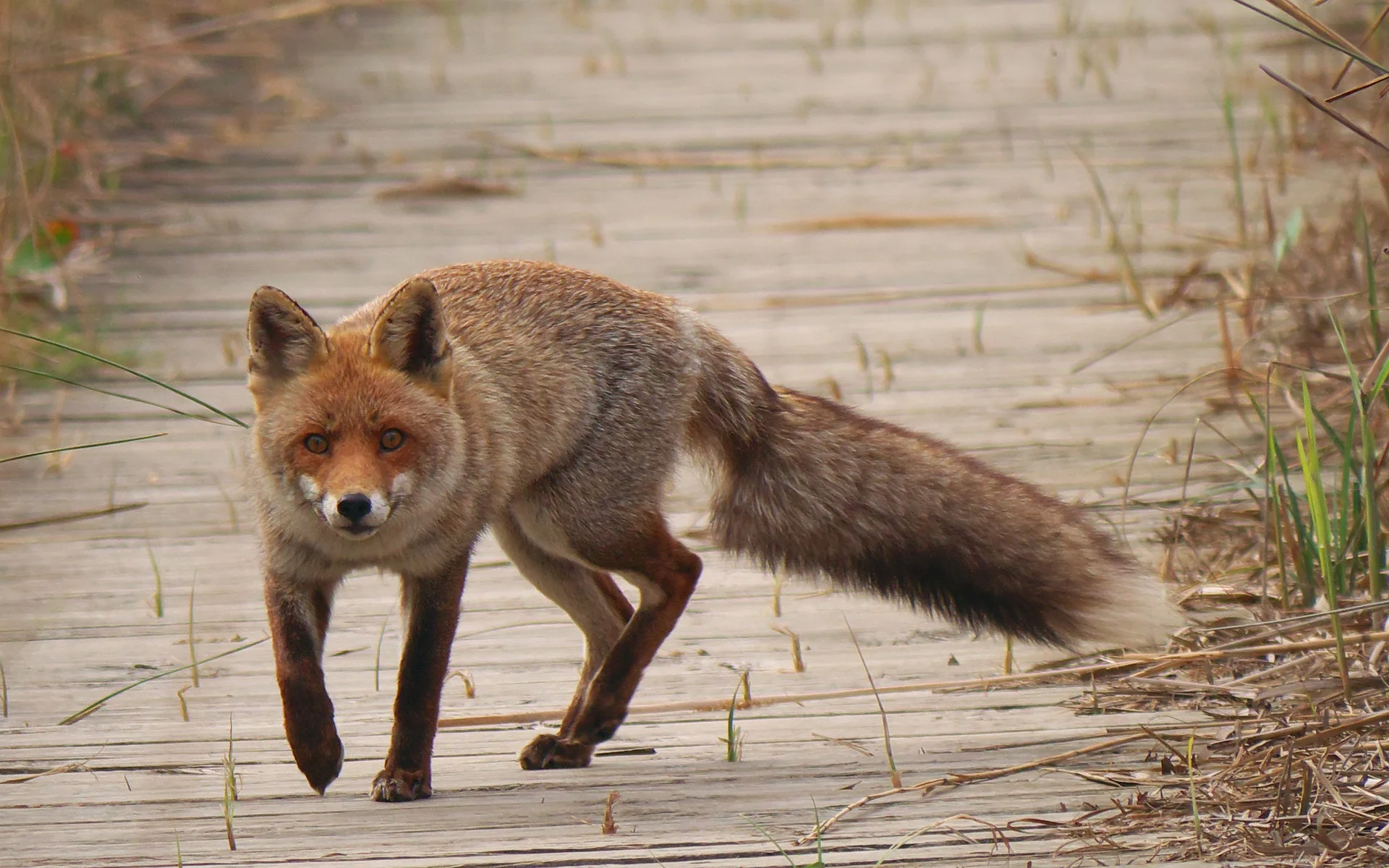
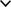Scientific name
The scientific name of the red fox is Vulpes vulpes.
Family
The red fox belongs to the family Canidae, the canid family, which includes several other carnivores such as wolves, coyotes, dogs and jackals.
Location
It has a very wide distribution and is found in a variety of habitats in the Northern Hemisphere. It is present throughout Europe, from arctic to Mediterranean areas.
The red fox is highly adaptable and can live in a variety of habitats, from forests and mountains to urban and suburban areas. Its wide distribution is partly due to its ability to adapt to different environmental and feeding conditions.
Behavior
Red foxes are territorial and mark their territories with urine and faeces to communicate with other foxes. Territories may vary in size depending on the availability of food and the sex of the individual.
They use a variety of sounds, including barks, growls and squeaks, as well as body language, to communicate with each other. They also have scent glands which they use to mark territory and communicate with other foxes.
Young foxes often disperse in search of new territories once they reach sexual maturity, which helps to maintain genetic diversity and colonise new areas.
Although most active at dawn and dusk, red foxes can also be active at night, especially in urban areas where they avoid human presence.
Feeding Habits
They are mainly carnivorous, but are also omnivorous in an opportunistic manner. They feed on a variety of prey, including rodents, rabbits, birds, insects, fruit and carrion. They usually hunt at dusk and dawn, but can also hunt during the day.
Reproduction
They have a breeding season that usually begins in late winter or early spring. Pairs may form temporary monogamous bonds during the breeding season. The dens are used as a refuge to raise their young, called cubs or young foxes.